How to do Tracing, Evaluation, and Observability for Google ADK

Manouk Draisma
Dec 23, 2025
Multi-agent architectures are quickly escaping the lab and showing up in real products. The challenge isn’t getting agents to work once it’s making them dependable when traffic increases, edge cases pile up, and failures become expensive. Google’s Agent Development Kit (ADK) simplifies how multiple agents are composed and coordinated, while LangWatch gives teams the tools to see what those agents are actually doing once they’re live.
In this article we will show how LangWatch makes agent behavior transparent by tracing decisions, tool usage, and inter-agent handoffs. The result is not just a working system, but one you can confidently monitor, debug, and improve in production.
Evaluation & Observability 🤝 Google ADK
A new way to build agent systems
Google’s Agent Development Kit approaches agent engineering from a developer-first perspective. Instead of prescribing strict patterns, it gives teams low-level building blocks to design, compose, and evolve multi-agent systems directly in Python. Native support for state handling, streaming responses, and lifecycle callbacks makes it well-suited for complex, long-running agent workflows. While it remains model-agnostic, it integrates especially well with Gemini models and Google Cloud’s Vertex AI, easing the transition from experimentation to large-scale deployment.
ADK stands out in a few key dimensions:
Composable Agent Structures
Design systems by assembling focused agents into layered or collaborative structures. ADK supports both fixed execution paths and dynamic routing driven by LLM decisions, making it adaptable to a wide range of use cases.Extensible Tooling
Agents can rely on built-in capabilities like search or code execution, while also incorporating external frameworks such as LangChain or LlamaIndex. Other agents can even be exposed as tools, allowing systems to interact with nearly any service or data source.Built for Production Environments
With first-class container support, cloud deployment integrations, and developer-facing tooling for evaluation and inspection via CLI and web interfaces, ADK reduces the friction between early prototypes and production-grade systems.
LangWatch: Observability for Agent Systems
ADK focuses on how agents are built and coordinated; LangWatch focuses on how they behave once real users are involved. Designed specifically for LLM-powered and agentic systems, LangWatch provides the visibility and evaluation layer teams need to operate agents safely and confidently in production environments.
LangWatch addresses the operational challenges of agent-based applications through a set of tightly integrated capabilities:
Agent Simulations
Analyze how agents make decisions across multi-step workflows, including tool selection, execution quality, and handoffs between agents. This makes it possible to identify failure modes that only appear in complex, real-world interactions.Feedback loops from Dev to Prod
Bring evaluation into the full lifecycle of your system. LangWatch supports workflows where automated judgments, regression tests, and production signals continuously inform improvements to prompts, models, and agent logic.Prompt and Behavior Iteration
Experiment with prompts, compare variants, and run controlled tests to understand how changes affect agent outcomes at scale—without relying on anecdotal feedback or manual inspection.Deep Runtime Visibility
By instrumenting agent systems with OpenTelemetry-compatible tracing, LangWatch captures each reasoning step, tool call, and state transition. This gives teams a clear view into otherwise non-deterministic agent behavior, enabling faster debugging and more reliable optimization.
Why the Integration Matters
Used together, ADK and LangWatch create a coherent workflow for the full lifecycle of agent-based systems—from initial design to long-term operation. ADK handles the coordination and execution of agents, while LangWatch focuses on understanding, evaluating, and improving their behavior in real-world conditions.
Because both rely on OpenTelemetry standards, agents built with ADK can emit traces and metrics that LangWatch consumes directly, without proprietary coupling or ecosystem lock-in. This open integration gives teams the freedom to evolve their stack while maintaining deep visibility and control as systems move from experimentation into production.
Implementation Walkthrough: Orchestrating Multi-Agent Systems with ADK and Instrumenting Them with LangWatch
This section walks through how to wire up a multi-agent system using Google ADK and layer in evaluation, tracing, and observability with LangWatch. The goal is to show how orchestration and runtime visibility come together in a practical setup.
Before getting started, make sure you have the following in place:
A Google Cloud project with billing configured
Vertex AI API enabled
A LangWatch account (a free tier is available)
Python 3.11 or newer, using Poetry for dependency management
Instrumentation with OpenInference
Interoperability with LangWatch SDK
You can use this integration together with the LangWatch Python SDK to add additional attributes to the trace:
How it works
The integration relies on standard OpenTelemetry instrumentation to capture what happens inside your agent system, without requiring invasive changes to your codebase.
langwatch.setup()
Bootstraps the LangWatch SDK and configures an OpenTelemetry exporter. Once initialized, your application is ready to emit traces from any library that supports OpenTelemetry instrumentation.ADK Instrumentation
The OpenInference-based instrumentor hooks directly into Google ADK internals, automatically generating spans for key execution events such as:Agent creation and lifecycle events
Tool invocations
Model requests and responses
Session and state transitions
Optional Trace Annotations
For cases where additional context is useful, the@langwatch.trace()decorator can be applied to enrich traces with custom metadata. This step is entirely optional and not required to get end-to-end visibility.
With this configuration in place, agent execution flows, tool usage, and model interactions are captured automatically and forwarded to LangWatch, giving you a detailed, end-to-end view of how ADK-based systems behave in practice.
With instrumentation in place, every agent decision, tool invocation, and transition between agents is emitted as structured trace data and sent to LangWatch automatically.
Observability in practice
Once traces start flowing, LangWatch reconstructs the full execution path of each request across the agent system:
Agent routing Visibility
Decisions made by the root agent and downstream agents are represented as nested traces, making it clear how requests move through the system and why one agent was selected over another at any given step.
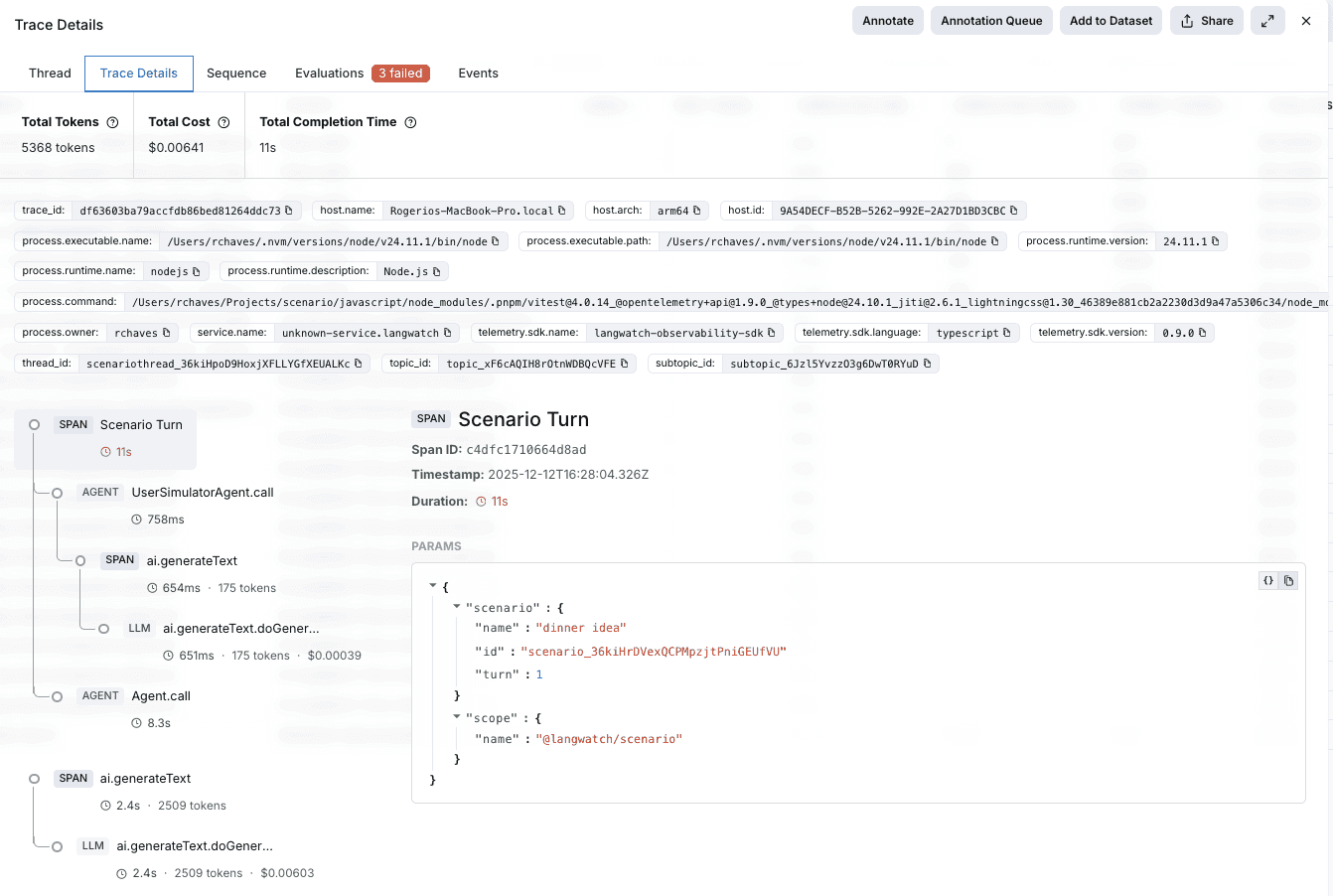
Cost and latency insights
LangWatch surfaces token usage across prompts, completions, and caching layers, alongside latency and cost metrics that can be mapped to the exact model and version in use.Tool execution analysis
Monitor how tools behave in real workloads by tracking invocation frequency, success rates, and response times. This makes it easy to spot unreliable integrations, slow external APIs, or tools that frequently fail under load.Inter-agent Coordination
When agents exchange context or delegate work, those interactions are captured as explicit transitions. This helps identify inefficiencies in coordination patterns and uncover bottlenecks across multi-agent workflows.
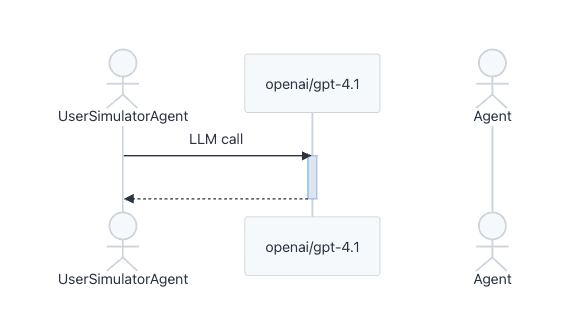
To support both high-level analysis and deep debugging, LangWatch offers multiple ways to explore this data from visual flow representations of agent execution to detailed, trace-level inspection of individual interactions.
Automated Agent Simulations
Observability gives you the raw execution data, but improving multi-agent systems requires more than inspecting traces after the fact. Traditional LLM evaluations fall short once agents start coordinating, delegating, and reasoning across multiple steps. Multi-agent systems need simulations that exercise full workflows, not isolated prompts.
LangWatch enables agent simulations tailored to the system’s real behavior, including:
Agent handoff robustness
Simulate scenarios where responsibility shifts between agents to verify that delegation happens at the right moment and with the correct context.Tool usage strategy
Test whether agents consistently select the right tools for a given situation, and how they recover when a tool fails or returns incomplete information.End-to-End agent trajectories
Evaluate complete execution paths across multiple steps to ensure the agent system follows a coherent and goal-oriented sequence when fulfilling user requests.
These simulations can be triggered automatically using synthetic scenarios. As new traces arrive, LangWatch can generate regression cases and surface failure patterns, shortening the feedback loop between detection and improvement and enabling continuous optimization of agent behavior.
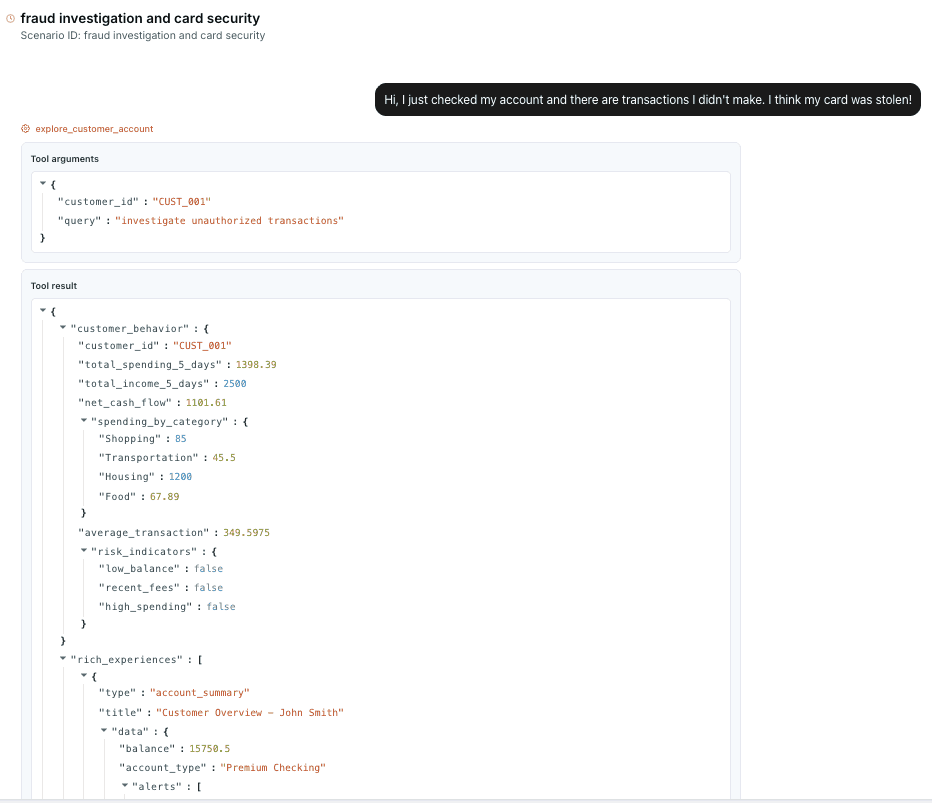
Improving agents through simulation and Experimentation
Once observability and agent simulations are in place, teams have the foundation needed to systematically improve multi-agent systems. Execution traces are captured automatically, enriched with simulation results, and labeled based on outcomes. When failures or regressions are detected, those traces can be grouped into datasets that represent real breakdowns in agent behavior.
These datasets form the basis for structured improvement workflows. In LangWatch, teams can route simulation failures into review queues for human analysis, annotate expected behavior, and turn high-quality examples into reusable reference datasets for ongoing testing.
From there, experimentation becomes data-driven rather than speculative. LangWatch enables teams to iterate on agent behavior by:
Side-by-Side behavior experiments
Run simulations using alternative agent instructions, policies, or model configurations and compare outcomes across complete agent trajectories—not just single responses.Scenario-Driven Agent Tuning
Production traces reveal recurring user intents and edge cases. These can be replayed as simulations to tune agent behavior for the situations that matter most, validating changes before they reach users.
By running controlled experiments against curated datasets, teams can test changes safely, compare alternatives, and promote improvements with confidence, closing the loop between observation, simulation, and deployment.
Experiment and A/B test with various system prompt and model changes in prompt playground. Validate the changes at scale by running the experiments on the regression dataset from the previous step.
Proactive Monitoring in Production
Improving agent systems isn’t a one-time effort. As usage grows and real-world conditions change, new failure modes and optimization opportunities continuously surface. LangWatch supports this ongoing feedback loop by providing monitoring, reporting, and alerting designed specifically for agent-based systems operating at scale.
Key capabilities include:
Cost and Efficiency Visibility
Track how models and tools are actually used in production, including execution time, token consumption, and downstream tool calls. This makes it possible to spot unnecessary complexity, eliminate redundant requests, and reserve more capable (and expensive) models for cases where they add real value.Behavioral Anomaly Detection
LangWatch highlights deviations in agent behavior, such as spikes in tool errors, unexpected routing changes, or shifts in decision patterns that may signal regressions or model drift.Simulation-Driven Feedback Loops
Real production interactions can be replayed as agent simulations, turning live data into test cases. Teams can use these scenarios to refine agent logic, update instructions, or improve tool implementations based on how users actually interact with the system.Custom KPIs and Alerts
Metrics derived from simulations and runtime signals can be aggregated into dashboards for operational and executive visibility. When key indicators degrade, alerts notify the right stakeholders before issues escalate.
Together, these capabilities help teams stay ahead of problems, continuously adapt their systems, and operate agent-based applications with confidence as they scale.
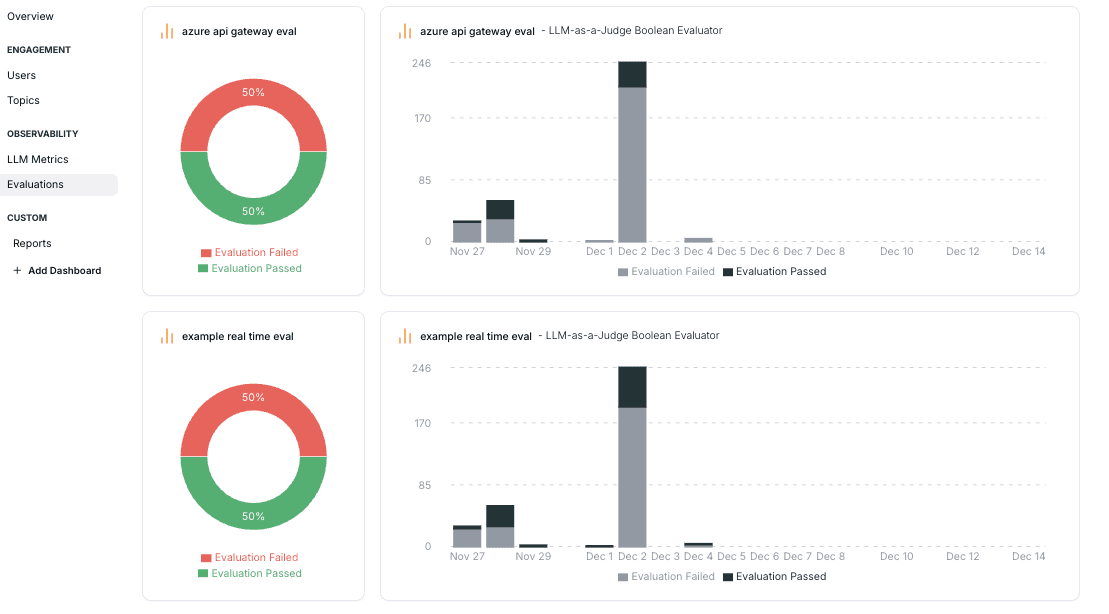
Build custom dashboards: For Product Management, Leadership and Dev.
Conclusion
What this architecture ultimately demonstrates is a practical answer to one of the hardest problems in agentic AI: moving from promising prototypes to systems that can be trusted in production. Google’s Agent Development Kit provides the structural foundation for building sophisticated, multi-agent workflows capable of handling real-world complexity. LangWatch complements this by delivering the observability, simulation, and monitoring capabilities required to operate those systems with confidence.
Together, ADK and LangWatch remove many of the friction points that have historically limited agent-based applications to demonstrations and proofs of concept. By combining robust orchestration with deep visibility and continuous feedback loops, teams can build agent systems that are not only powerful, but also reliable, measurable, and improvable over time.
As agent frameworks mature and models continue to advance, the differentiator will no longer be who can build agents—but who can operate them well. Organizations that invest early in strong development, simulation, and observability practices will be best positioned to scale agentic AI responsibly. ADK and LangWatch provide a solid foundation for building that future.


